Introduction
The DataWave project provides a general purpose framework to facilitate persistence, indexing and retrieval of both structured and unstructured textual objects. Central to DataWave’s design is that it leverages Apache Accumulo to implement a flexible data model and to implement ingest and query components that are robust and scalable.
Common use cases for DataWave include…
- Data fusion across disparate datasets via DataWave’s document-oriented approach to persistence, indexing and retrieval of objects
- Multi-tenant data architectures, with tenants having distinct security requirements and data access patterns
- Construction and analysis of distributed graphs
Security
DataWave provides flexible and extensible data security features predicated on Accumulo’s security model. As a result, organizations can apply either coarse- or fine-grained access controls to their data, and they can leverage DataWave’s security API to apply custom role-based access controls for their users.
System Architecture
DataWave’s ingest and query components are loosely coupled to one another and may be configured to operate on distinct clusters, if desired. For example, in the configuration shown below, ingest services are segregated from query services so that CPU, memory, and network resources within the data warehouse cluster may be prioritized for query processing.
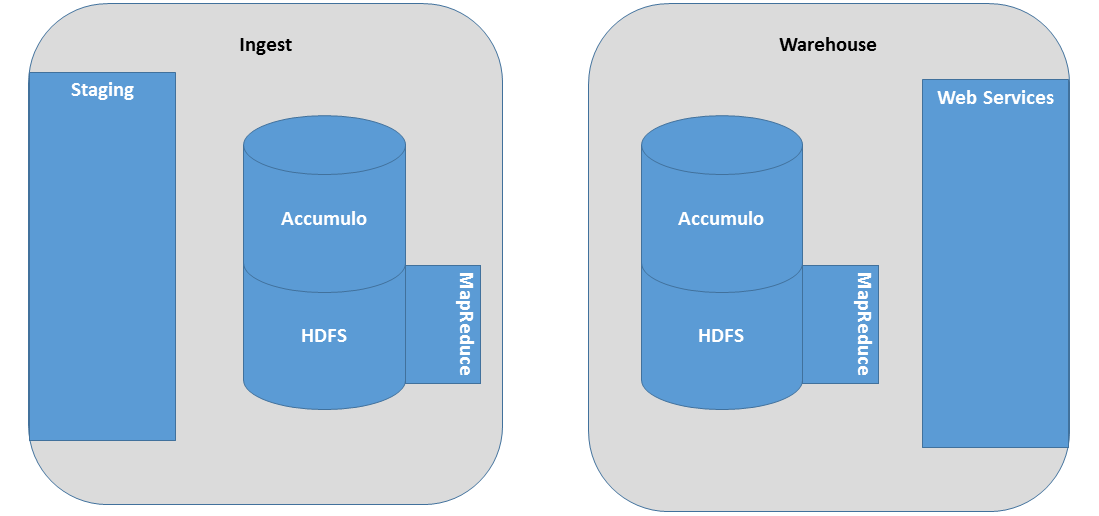
If resource contention between ingest processing and query processing is not a primary concern, then DataWave may be hosted on a single, shared cluster environment. From the perspective of DataWave’s ingest and query applications, selecting one of these two deployment strategies is a matter of adjusting a handful of application settings.
Regardless of the deployment strategy, the flow of data into and out of the system remains largely the same. Raw data to be ingested may arrive in a staging area for pre-processing, if needed, or it may be written directly to HDFS. Once the input data arrives in HDFS, DataWave will process it via MapReduce and ultimately write the MapReduce output to DataWave’s Accumulo tables in the data warehouse. Lastly, query clients utilize various web services exposed through DataWave’s REST API to retrieve data of interest from the warehouse Accumulo repository.